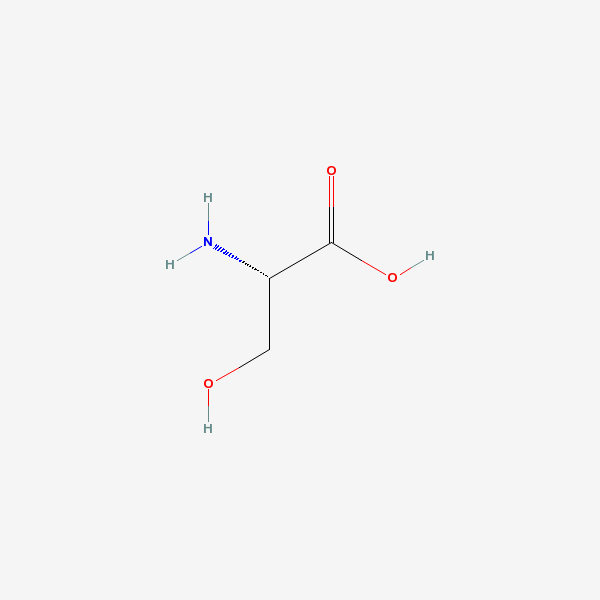
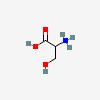
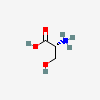
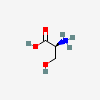
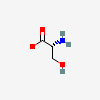
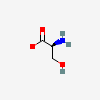
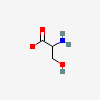
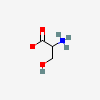
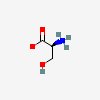
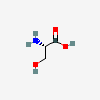
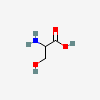
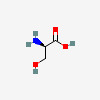
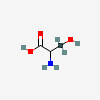
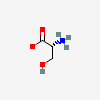SERINE
 PubChem Notes:
PubChem Notes:
Serine A non-essential amino acid occurring in natural form as the L-isomer. It is synthesized from GLYCINE or THREONINE. It is involved in the biosynthesis of PURINES; PYRIMIDINES; and other amino acids.
Ser - definition from Biology-Online.org
[(Science: cell biology) An internal membrane structure of the eukaryotic cell. Biochemically similar to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, but lacks the ribosome binding function. Tends to be tubular rather than sheet like, may be separate from the rough endoplasmic reticulum or may be an extension of it. abundant in cells concerned with lipid metabolism and proliferates in hepatocytes when animals are challenged with lipophilic drugs. Acronym: SER
MediLexicon serine - Medical Dictionary Definition for Term 'serine'
[1. the l-isomer is one of the amino acids occurring in proteins.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
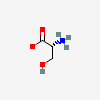
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|