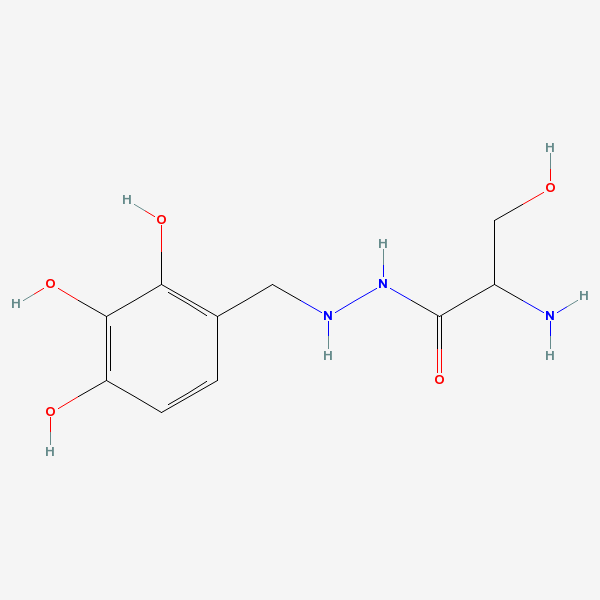
Serazide
 PubChem Notes:
PubChem Notes:
Benserazide An inhibitor of DOPA DECARBOXYLASE that does not enter the central nervous system. It is often given with LEVODOPA in the treatment of parkinsonism to prevent the conversion of levodopa to dopamine in the periphery, thereby increasing the amount that reaches the central nervous system and reducing the required dose. It has no antiparkinson actions when given alone.
MediLexicon benserazide - Medical Dictionary Definition for Term 'benserazide'
[1. An l-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (dopa decarboxylase) inhibitor resembling carbidopa in action; given in combination with levodopa as an antiparkinsonian regimen. The benserazide prevents peripheral destruction of levodopa and thus reduces cardiovascular side effects of treatment.
Molecular Formula:
C10H15N3O5
InChI: InChI=1/C10H15N3O5/c11-6(4-14)10(18)13-12-3-5-1-2-7(15)9(17)8(5)16/h1-2,6,12,14-17H,3-4,11H2,(H,13,18)/f/h13H
InChIKey: InChIKey=BNQDCRGUHNALGH-NDKGDYFDCE
SMILES: C1=CC(=C(C(=C1CNNC(=O)C(CO)N)O)O)O
Names:
Benserazida [INN-Spanish]
Benserazide [USAN:BAN:INN]
benserazide
Benserazidum [INN-Latin]
BRN 3984490
DL-Serine 2-(2,3,4-trihydroxybenzyl)hydrazide
DL-Seryltrihydroxybenzylhydrazine
Madopa
Ro 4-4602
Serazide
2-amino-3-hydroxy-N'-[(2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl)methyl]propanehydrazide
Registries:
PubChem CID 2327
PubChem ID 152671
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|