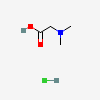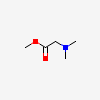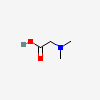trimethylglycocoll
 PubChem Notes:
PubChem Notes:
Betaine A naturally occurring compound that has been of interest for its role in osmoregulation. As a drug, betaine hydrochloride has been used as a source of hydrochloric acid in the treatment of hypochlorhydria. Betaine has also been used in the treatment of liver disorders, for hyperkalemia, for homocystinuria, and for gastrointestinal disturbances. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p1341)
Betaine - definition from Biology-Online.org
[(Science: chemical) a derivative of glycine characterised by high water solubility. Can function as an osmotic agent in plant tissues. See: biogenic amines.
MediLexicon betaine - Medical Dictionary Definition for Term 'betaine'
[1. An oxidation product of choline and a transmethylating intermediate in metabolism.2. A class of compounds related to betaine. (1) (R3N+—CHR′—COO−), glycine betaine.
Molecular Formula:
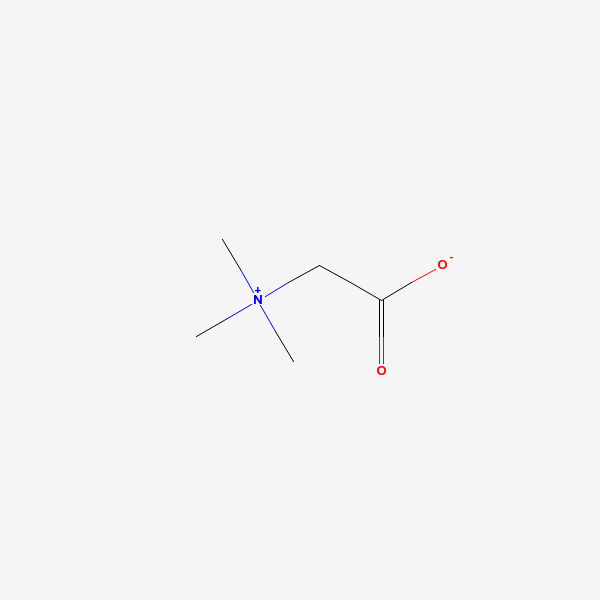
C5H11NO2
InChI: InChI=1/C5H11NO2/c1-6(2,3)4-5(7)8/h4H2,1-3H3
InChIKey: InChIKey=KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYAI
SMILES: C[N+](C)(C)CC([O-])=O
CAS number 107-43-7
Names:
abromine
betaine
Betaine
betaine
Betaine
Glycine betaine
glycine betaine
Methanaminium, 1-carboxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-, hydroxide, inner salt
N,N,N-trimethylammonioacetate
N,N,N-Trimethylglycine
Trimethylaminoacetate
Trimethylammonioacetate
trimethylammonioacetate
trimethylglycocoll
(trimethylammoniumyl)acetate
1-carboxy-N,N,N-trimethylmethanaminium inner salt
2-trimethylammonioacetate
Registries:
PubChem CID 247
Beilstein =3537113
CAS 107-43-7 (from NIST)
ChEBI 17750
Gmelin 26434
Kegg C00719
PubChem ID 10503467
PubChem ID 3985
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|