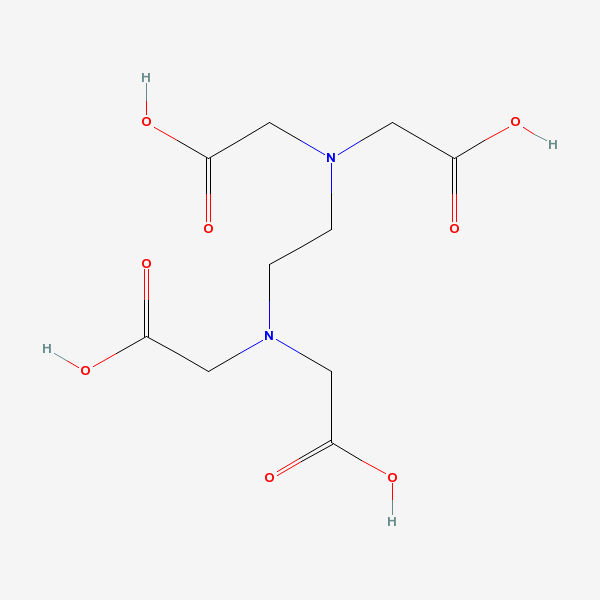
Metal chelating agent
 Chelating agents - definition from Biology-Online.org
Chelating agents - definition from Biology-Online.org
[organic chemicals that form two or more coordination bonds with a central metal ion. Heterocyclic rings are formed with the central metal atom as part of the ring. Some biological systems form metal chelates, e.g., the iron-binding porphyrin group of haemoglobin and the magnesium-binding chlorophyll of plants. They are used chemically to remove ions from solutions, medicinally against microorganisms, to treat metal poisoning, and in chemotherapy protocols.
MediLexicon EDTA - Medical Dictionary Definition for Term 'EDTA'
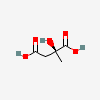
[1. Abbreviation for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
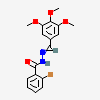
|
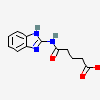
|
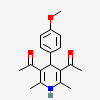
|
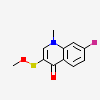
|
|
|
|
|